BLOG
May 23,2024
Healthcare's Many Faces: What Is a Urologist?
When it comes to healthcare, each medical speciality plays a critical role in ensuring comprehensive care for patients. One such speciality, which might not be as widely known among the general public, is urology. A urologist is a medical professional specialized in the diagnosis and treatment of disorders related to the urinary system and the male reproductive organs.
Here’s a guide on what a Urologist does and why you might need one:
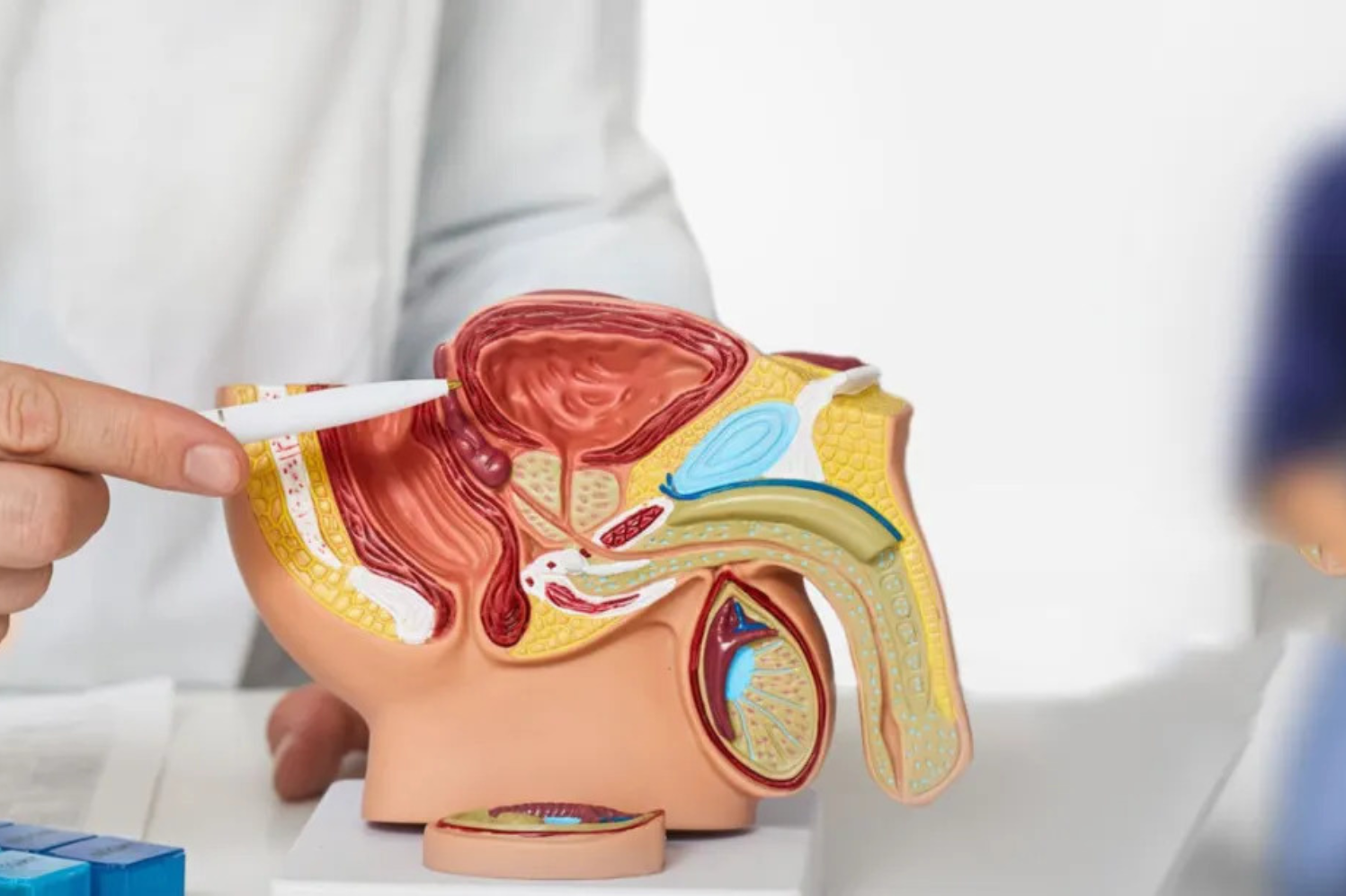
Who is a Urologist?
Urologists are highly trained surgeons who focus on treating diseases and disorders of the urinary tract and the male reproductive system. This includes organs such as the kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra, and the male genitals including the penis, testes, scrotum, and prostate. Urologists undergo extensive training, typically completing a five-year residency after medical school, where they learn both surgical and non-surgical treatments.
Conditions Treated by Urologists
Urologists are vital in diagnosing and treating a broad spectrum of conditions affecting the urinary tract and male reproductive organs. Here's a more detailed look at some of the primary conditions they handle:
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
UTIs occur when bacteria enter and infect the urinary tract, which includes the kidneys, bladder, and urethra. Symptoms may include a strong, persistent urge to urinate, a burning sensation during urination, passing frequent, small amounts of urine, and urine that appears cloudy or red. While women are generally more susceptible to UTIs due to their anatomy, men can also suffer from these infections, particularly older men with prostate problems.
Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are hard mineral and salt deposits that form inside the kidneys. They often result from concentrated urine, allowing minerals to crystallize and stick together. Passing kidney stones can be extremely painful and may cause symptoms like severe pain in the side and back, below the ribs, pain that radiates to the lower abdomen and groin, pain during urination, and pink, red, or brown urine. Urologists might recommend drinking lots of fluids and pain relievers for small stones. For larger stones, medical procedures like lithotripsy or surgical removal may be necessary.
Bladder Issues
Urologists treat various bladder problems, including:
- Overactive Bladder (OAB): Characterized by sudden urges to urinate that are difficult to control.
- Urinary Incontinence: The involuntary leakage of urine, which can occur from stress (coughing or sneezing) or an urge that cannot be stopped.
- Bladder Prolapse: More common in women, this occurs when the bladder sags into the vagina. Treatments range from pelvic floor exercises to surgical repair.
Prostate Disorders
Common prostate disorders include:
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): Enlargement of the prostate gland which can block the flow of urine out of the bladder, causing bladder, urinary tract, or kidney problems.
- Prostatitis: Inflammation of the prostate, which can cause painful or difficult urination.
- Prostate Cancer: One of the most common cancers in men, which may need treatments ranging from surveillance to surgery depending on its severity.
Male Infertility
Issues with male fertility can stem from various factors including sperm production, sperm delivery, and hormone levels. Urologists often work with reproductive specialists to determine the cause of infertility and may suggest treatments or procedures like surgery for varicoceles or medication for hormonal imbalances.
Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
ED is defined as the inability to achieve or maintain an erection suitable for sexual intercourse. Causes can be both psychological and physical, including diabetes, heart disease, and more. Urologists typically address this with medication, therapies, or even surgery, depending on underlying causes.
Urologic Oncology
Urologic oncologists specialize in treating cancers of the urinary system and male reproductive organs, including the bladder, kidneys, prostate, and testicles. Treatments vary based on the cancer type and may include surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, or immunotherapy.
Pediatric Urology
This subspecialty deals with urologic disorders in children, such as:
- Bedwetting: Often related to developmental stages or issues like urinary tract infections.
- Undescended Testes: A condition where one or both of the male testes have not descended into the scrotal sac.
- Congenital Abnormalities: Such as abnormalities in the urinary tract structure that need to be corrected surgically.
These conditions highlight the extensive scope of urology and underline the importance of this specialty in managing not only common urinary issues but also complex reproductive and oncological concerns. Whether addressing common urinary disorders or complex surgical needs, urologists play a crucial role in enhancing patient health and quality of life through specialized care.
Diagnostic and Treatment Procedures
Urologists are equipped to perform a variety of diagnostic and treatment procedures. Some of the most common include:
- Cystoscopy: A procedure that allows the urologist to see inside the bladder and urethra using a camera.
- Urodynamic Testing: Measures how well the bladder, urethra, and sphincters hold and release urine.
- Prostate Biopsy: A critical procedure in diagnosing prostate cancer, involving the removal of small samples of prostate tissue.
- Lithotripsy: A non-invasive method to break up kidney stones using shock waves.
- Vasectomy: A surgical procedure for male sterilization or permanent contraception.
- Penile Implants: For treating severe cases of erectile dysfunction.
- Surgical Procedures: Such as removing tumors or correcting structural abnormalities in the urinary tract and reproductive organs.
When to See a Urologist
Knowing when to see a urologist is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment, improving outcomes. Consider consulting a urologist if you experience:
- Persistent pain or irritation in the lower back, pelvis, sides, or genital area.
- Changes in urination, like increased frequency, urgent need, pain during urination, or weak stream.
- Blood in urine, which may indicate various conditions, including cancer.
- Erectile dysfunction or infertility issues after trying to conceive for a year.
For expert advice and treatment, Dr. Karthikeyan can help. Book an appointment today.
Copyright © . Karthikeyan V S. All Rights Reserved.
Powered By: Cortex Media Marketing Pvt Ltd


