Infertility – What to know?
Inability to conceive despite one year of trying adequately. In up to 50% couples, male factor is the reason for infertility.
Common causes of male infertility
What basics to know about infertility
You should have an idea of the normal male and female reproductive tracts and the basic idea of sperm and egg.
There are roughly 4 stages in conception.
Men produce millions of sperms though only one sperm is necessary to fuse with the egg. Sperm production usually continues even beyond 40-45 years though numbers and quality may reduce and genetic defects are possible beyond paternal age of 40.
Women produce a fixed number of eggs throughout their reproductive period (~15-45 years). So it is very important not to waste the eggs during infertility treatment. All treatment on women work through induction of ovulation, i.e., increasing the egg production. This leads to reduced egg reserve and eggs may not be available when all other problems are sorted out.

Low sperm count – how low is low
Oligospermia is defined as sperm counts less than 16 million per ml. Based on AUA guidelines, severe oligospermia is defined as sperm counts less than 5 million per ml.

Normal Sperm Count
Low Sperm Count

What are the causes for low sperm count?
Varicocele
Hypogonadism
Genetic
Idiopathic
Retrograde ejaculation
Testicular failure
Male accessory gland infection (MAGI)
Partial obstruction of ejaculatory ducts
Treatment for oligospermia – Non - medical therapy
Reduce stress.
Do some exercise every day.
Sleep well.
Maintain an appropriate weight.
Maintain a BMI of around 19-25. You can use online calculators to find out your BMI.
Eat healthy diet; Reduce carbohydrates. Add more proteins in your diet and keep calorie count as a guide.
Drugs (Careful decision is required for drug treatment in oligospermia)
Clomifene citrate
HCG/FSH
Antioxidants
Anastrozole
Surgical
Microsurgical varicocele repair
Transurethral resection of ejaculatory duct obstruction (in case of obstruction)
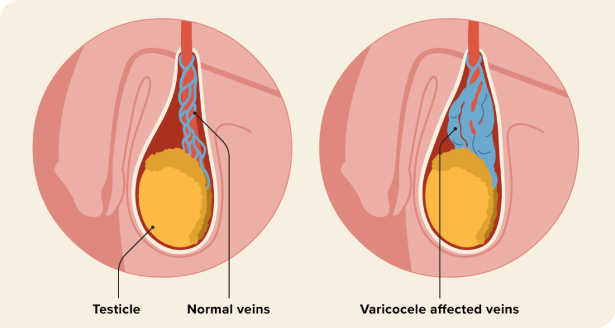
Varicocele
Varicocele means enlarged veins around the testis leading to damage of the testis and sperms
Varicocele leads to reduced counts or reduced quality of sperms
Varicocele is an important cause of male infertility
Microsurgical varicocelectomy is the gold standard operation for varicocele
Azoospermia
Azoospermia – absent sperms in semen

Normal Sperms
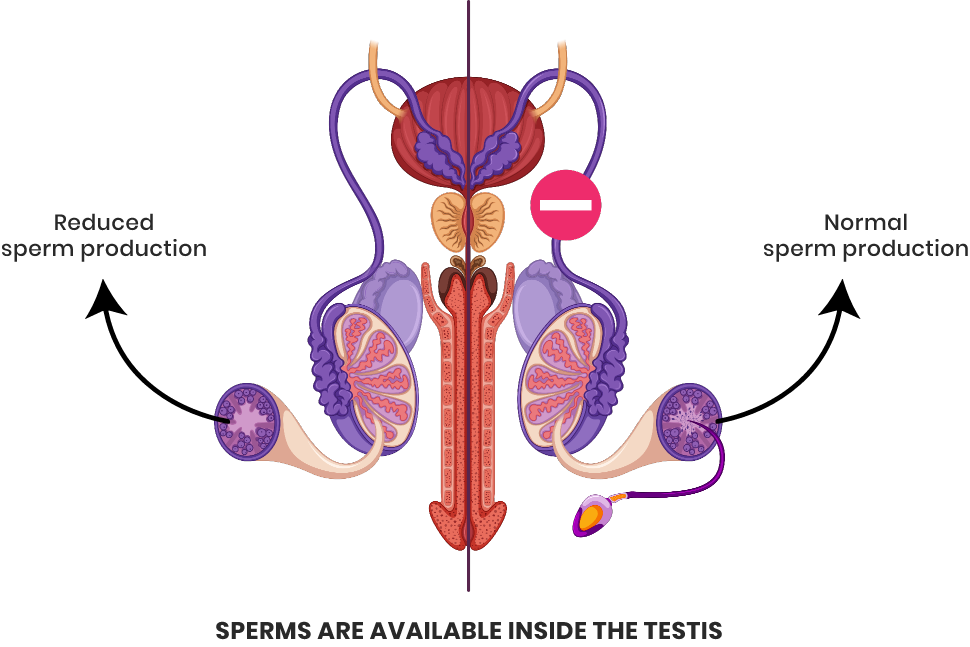
Azoospermia

Azoospermia
Azoospermia is defined as the absence of sperms in semen

There are 2 major types
Non-obstructive
In patients with no block to sperm passage, the production itself is very less, however sperms may be available inside the testis.
Obstructive
There may be good production of sperms but due to block in passage none of the sperms can reach the semen.
Micro TESE – Microdissection Testicular Sperm Extraction
Non Obstructive Azoospermia (NOA) is a condition where there are no sperms in the ejaculate. Traditionally they were considered infertile With the advent of operating microscopes and the ICSI (Intra Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection) technique. Micro TESE is able to help these men father their own children
In this technique, the male undergoes rigorous evaluation as to why he developed azoospermia in the first place. Once we are sure with the genetic constitution of the male, we plan for sperm retrieval. Initially a TESA is done to identify if sperms can be retrieved.
If TESA is negative for sperms, in the same sitting, Micro TESE is done.
MicroTESE is done by bivalving the testis under the operating microscope (15-20 X) and sperm bearing seminiferous tubules are identified by experience. Once these tubules are identified, they are teased and the embryologist under the light microscope identifies sperms and their quality.
This procedure is carried out religiously and untiringly till we get the apt quality of sperms for ICSI. There are few conditions like Sertoli only cell syndrome, where the chances of sperm retrieval is only 5% but we should note that one good sperm can be enough for a successful ICSI.

Treatment options for infertility
Natural conception: Here the male and female partners are deemed normal after testing. The male should be able to deposit semen deep inside the birth passage of his wife. Semen should stay in the vagina for at least 4-6 hours before it can ascend through the uterus and reach the tube to meet the egg. Egg is released around 9 days of completion of periods (for 5 days bleed usually). The concept of fertile period is important and it can vary from person to person and sometimes between cycles. A safe estimate is to have alternate day sex roughly around the same time from day 7 or 2-3 days after bleeding has stopped and continue for at least 12-14 days or till onset of bleeding. If you are unable to conceive for 1 year of proper trying (will be defined by your doctor) then you may need assisted reproductive techniques despite everything being normal due to unknown factors.
Assisted reproductive techniques:
While performing ART, male sperm treatment should be optimized to match the plan of the wife. Wife should be evaluated for egg production and patency of tubes. Egg monitoring is done by serial scans to see if egg is produced and released and the number of days for ovulation. For successful ART wife should be at least 35 years old. Chance of successful ART and pregnancy is reduced with advancing age of mother. In case of repeated abortions, there is a need for further testing and you should discuss this with your doctor.
IUI
IUI is the simplest form of ART with a reasonable success especially when the wife is young. Here the semen of husband is injected into the uterus. Ovulation induction may be done in woman and the timing of IUI is fixed based on egg monitoring. This is the cheapest form of ART.
IVF & ICSI
IVF & ICSI Here eggs are retrieved from the ovary and are fused in vitro (outside the human body) with sperms and the embryo is placed back inside the uterus. Once successful then it continues like a normal pregnancy. In ICSI the sperm is injected into the egg directly. Success is obviously best with ICSI and next best is IVF, and so is the cost.
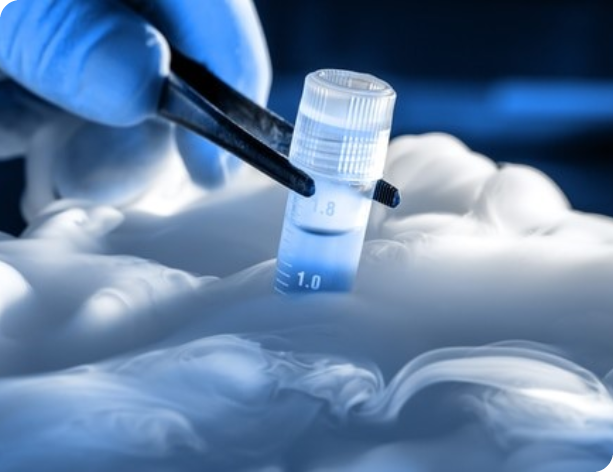
Cryopreservation
When sperm production is at fault and there is no much improvement with medicines, it means that there is a possibility of sperms becoming very less. This situation can happen in patients with severe low counts, varicocele and sometimes premarital. Preservation is done in liquid nitrogen at -160 degree C and it can stay good for at least 3-5 years. In case sperms do not improve or there is long time to plan for children, cryopreservation is handy. One should know that only 50% sperms retrieved from cryopreserved samples stay good. This means that patients with low counts to start with may have poor yield. However since the number of sperms needed in IVF or ICSI is very less (20-30), it is usually possible to retrieve healthy sperms from cryopreserved samples. In patients undergoing cancer treatment in the form of radiation or chemotherapy it is wise to store sperms as they can be damaged. This can be done for eggs and embryos as well.
Copyright © . Karthikeyan V S. All Rights Reserved.
Powered By: Cortex Media Marketing Pvt Ltd


